Raspberry Pi 4 实时推理(30 fps!)
创建于:2025 年 4 月 1 日 | 最后更新:2025 年 4 月 1 日 | 最后验证:2024 年 11 月 5 日
作者:Tristan Rice
PyTorch 原生支持 Raspberry Pi 4。本教程将指导您如何设置 Raspberry Pi 4 以运行 PyTorch,并在 CPU 上实时运行 MobileNet v2 分类模型(30 fps+)。
所有测试均在 Raspberry Pi 4 Model B 4GB 上进行,但应与 2GB 版本兼容,在 3B 上运行性能会降低。

前提条件 _
遵循本教程需要 Raspberry Pi 4、相应的摄像头以及其他所有标准配件。
散热片和风扇(可选但推荐)
5V 3A USB-C 电源适配器
SD 卡(至少 8GB)
SD 卡读写器
Raspberry Pi 4 设置指南
PyTorch 只为 Arm 64 位(aarch64)提供 pip 软件包,因此您需要在 Raspberry Pi 上安装 64 位版本的操作系统
您可以从 https://downloads.raspberrypi.org/raspios_arm64/images/ 下载最新的 arm64 Raspberry Pi OS,并通过 rpi-imager 进行安装。
32 位 Raspberry Pi OS 将无法使用。

安装时间至少需要几分钟,具体取决于您的网络速度和 SD 卡速度。安装完成后,它应该看起来像:
现在是时候将你的 SD 卡放入树莓派中,连接摄像头并启动它了。
启动并完成初始设置后,你需要编辑 /boot/config.txt 文件以启用摄像头。
# This enables the extended features such as the camera.
start_x=1
# This needs to be at least 128M for the camera processing, if it's bigger you can just leave it as is.
gpu_mem=128
# You need to commment/remove the existing camera_auto_detect line since this causes issues with OpenCV/V4L2 capture.
#camera_auto_detect=1
然后重启。重启后,应该存在 video4linux2 设备 /dev/video0 。
安装 PyTorch 和 OpenCV
PyTorch 和其他所有我们需要的库都有 ARM 64 位/aarch64 版本,因此您只需通过 pip 安装它们,就可以像任何其他 Linux 系统一样使用它们。
$ pip install torch torchvision torchaudio
$ pip install opencv-python
$ pip install numpy --upgrade
我们现在可以检查一切是否安装正确:
$ python -c "import torch; print(torch.__version__)"
视频捕获
对于视频捕获,我们将使用 OpenCV 来流式传输视频帧,而不是更常见的 picamera 。picamera 在 64 位 Raspberry Pi OS 上不可用,并且比 OpenCV 慢得多。OpenCV 直接访问 /dev/video0 设备以抓取帧。
我们所使用的模型(MobileNetV2)接受 224x224 大小的图像,因此我们可以直接从 OpenCV 以 36fps 的速度请求它。我们针对模型的帧率是 30fps,但我们请求略高于这个帧率,以确保始终有足够的帧。
import cv2
from PIL import Image
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH, 224)
cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT, 224)
cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS, 36)
OpenCV 返回一个 BGR 格式的 numpy 数组,因此我们需要读取并进行一些调整以将其转换为预期的 RGB 格式。
ret, image = cap.read()
# convert opencv output from BGR to RGB
image = image[:, :, [2, 1, 0]]
这种数据读取和处理大约需要 3.5 ms 。
图像预处理 §
我们需要将帧转换为模型期望的格式。这与您在标准 torchvision transforms 上进行的处理相同。
from torchvision import transforms
preprocess = transforms.Compose([
# convert the frame to a CHW torch tensor for training
transforms.ToTensor(),
# normalize the colors to the range that mobilenet_v2/3 expect
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]),
])
input_tensor = preprocess(image)
# The model can handle multiple images simultaneously so we need to add an
# empty dimension for the batch.
# [3, 224, 224] -> [1, 3, 224, 224]
input_batch = input_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
模型选择 §
您可以选择多种模型,它们具有不同的性能特性。并非所有模型都提供预训练的变体,因此出于测试目的,您应选择一个提供预训练变体的模型,但如果您训练并量化自己的模型,则可以使用任何模型。
由于它具有良好的性能和准确性,我们在此教程中使用 mobilenet_v2 。
Raspberry Pi 4 性能测试结果:
Model |
FPS |
总耗时(毫秒/帧) |
模型耗时(毫秒/帧) |
qnnpack 预训练模型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
mobilenet_v2 |
33.7 |
29.7 |
26.4 |
True |
mobilenet_v3_large |
29.3 |
34.1 |
30.7 |
True |
resnet18 |
9.2 |
109.0 |
100.3 |
False |
resnet50 |
4.3 |
233.9 |
225.2 |
False |
resnext101_32x8d |
1.1 |
892.5 |
885.3 |
False |
inception_v3 |
4.9 |
204.1 |
195.5 |
False |
googlenet |
7.4 |
135.3 |
132.0 |
False |
shufflenet_v2_x0_5 |
46.7 |
21.4 |
18.2 |
False |
shufflenet_v2_x1_0 |
24.4 |
41.0 |
37.7 |
False |
shufflenet_v2_x1_5 |
16.8 |
59.6 |
56.3 |
False |
shufflenet_v2_x2_0 |
11.6 |
86.3 |
82.7 |
False |
MobileNetV2:量化与即时编译
为了获得最佳性能,我们希望有一个已经量化和融合的模型。量化意味着它使用 int8 进行计算,这比标准的 float32 数学性能要高得多。融合意味着尽可能地将连续的操作融合成一个更高效的版本。通常,像激活( ReLU )这样的东西可以合并到推理之前的层( Conv2d )中。
PyTorch 的 aarch64 版本需要使用 qnnpack 引擎。
import torch
torch.backends.quantized.engine = 'qnnpack'
在本例中,我们将使用 torchvision 提供的预量化和融合的 MobileNetV2 版本。
from torchvision import models
net = models.quantization.mobilenet_v2(pretrained=True, quantize=True)
我们接下来希望将模型进行 jit 以减少 Python 开销并融合任何操作。Jit 将帧率从没有它时的约 20fps 提升到约 30fps。
net = torch.jit.script(net)
整合
我们现在可以将所有部件组合起来并运行:
import time
import torch
import numpy as np
from torchvision import models, transforms
import cv2
from PIL import Image
torch.backends.quantized.engine = 'qnnpack'
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0, cv2.CAP_V4L2)
cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH, 224)
cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT, 224)
cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS, 36)
preprocess = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]),
])
net = models.quantization.mobilenet_v2(pretrained=True, quantize=True)
# jit model to take it from ~20fps to ~30fps
net = torch.jit.script(net)
started = time.time()
last_logged = time.time()
frame_count = 0
with torch.no_grad():
while True:
# read frame
ret, image = cap.read()
if not ret:
raise RuntimeError("failed to read frame")
# convert opencv output from BGR to RGB
image = image[:, :, [2, 1, 0]]
permuted = image
# preprocess
input_tensor = preprocess(image)
# create a mini-batch as expected by the model
input_batch = input_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
# run model
output = net(input_batch)
# do something with output ...
# log model performance
frame_count += 1
now = time.time()
if now - last_logged > 1:
print(f"{frame_count / (now-last_logged)} fps")
last_logged = now
frame_count = 0
运行它显示我们大约在 30 fps 左右。
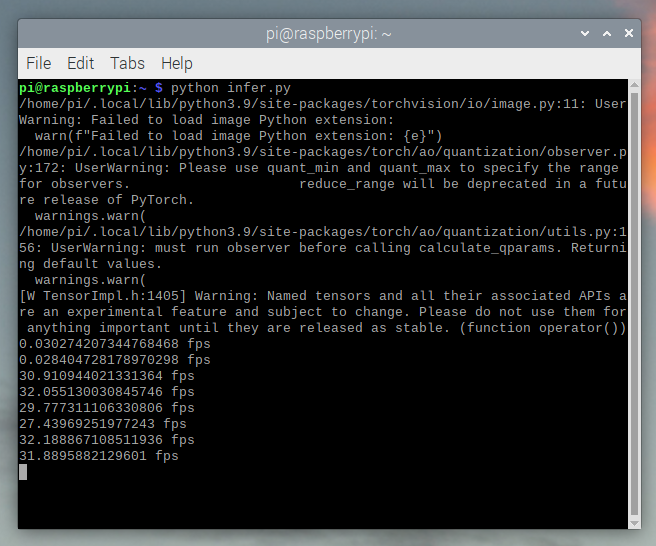
这是在 Raspberry Pi OS 的所有默认设置下进行的。如果你禁用了 UI 以及所有默认启用的其他后台服务,它的性能和稳定性会更好。
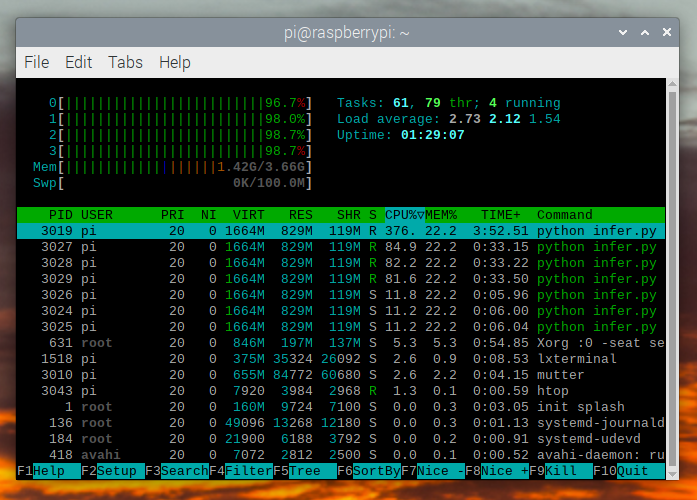
如果我们检查 htop ,我们会看到我们几乎有 100%的利用率。
为了验证其端到端的工作情况,我们可以计算类别的概率并使用 ImageNet 类别标签来打印检测到的结果。
top = list(enumerate(output[0].softmax(dim=0)))
top.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
for idx, val in top[:10]:
print(f"{val.item()*100:.2f}% {classes[idx]}")
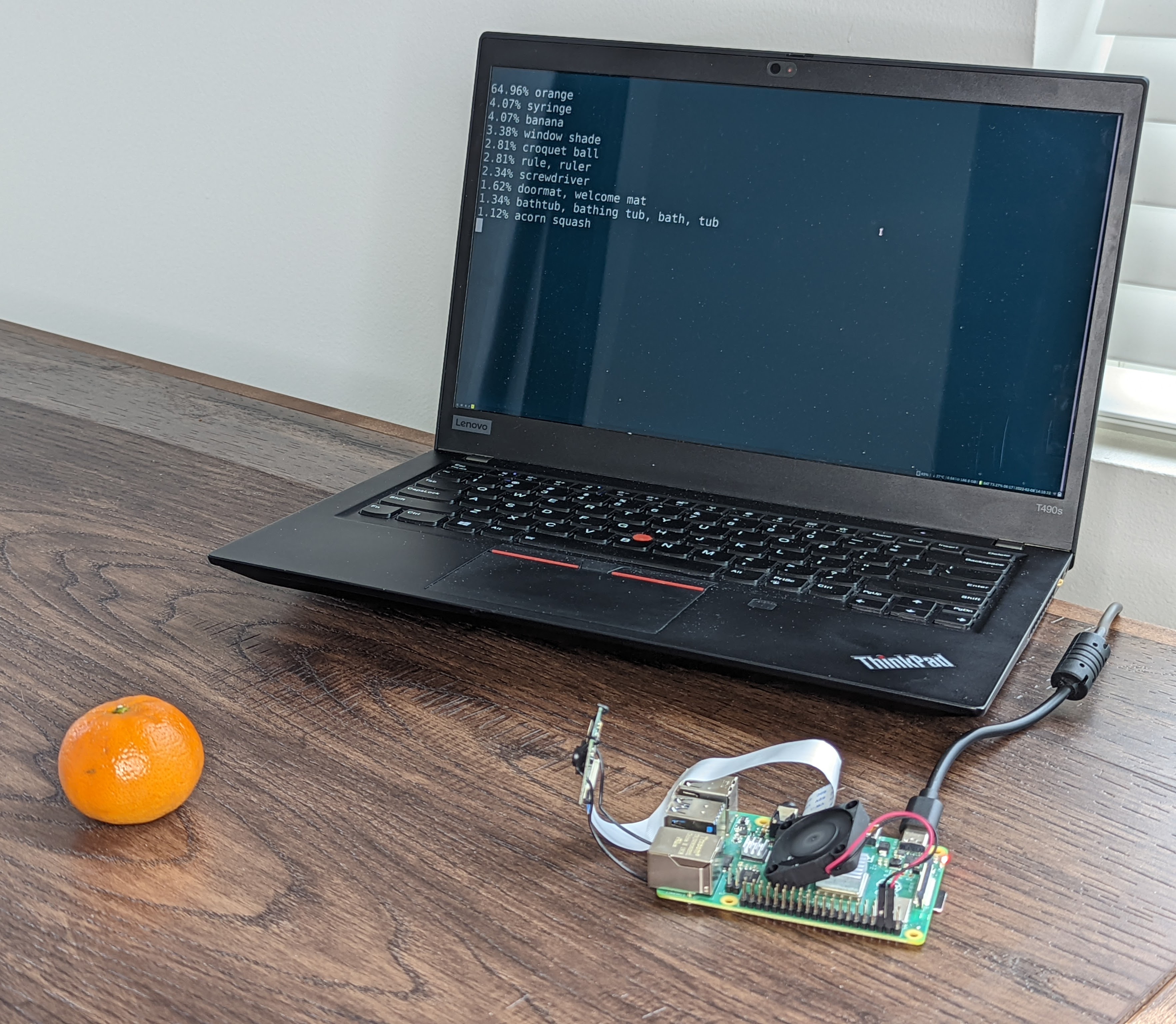
mobilenet_v3_large 实时运行:

检测到橙子:

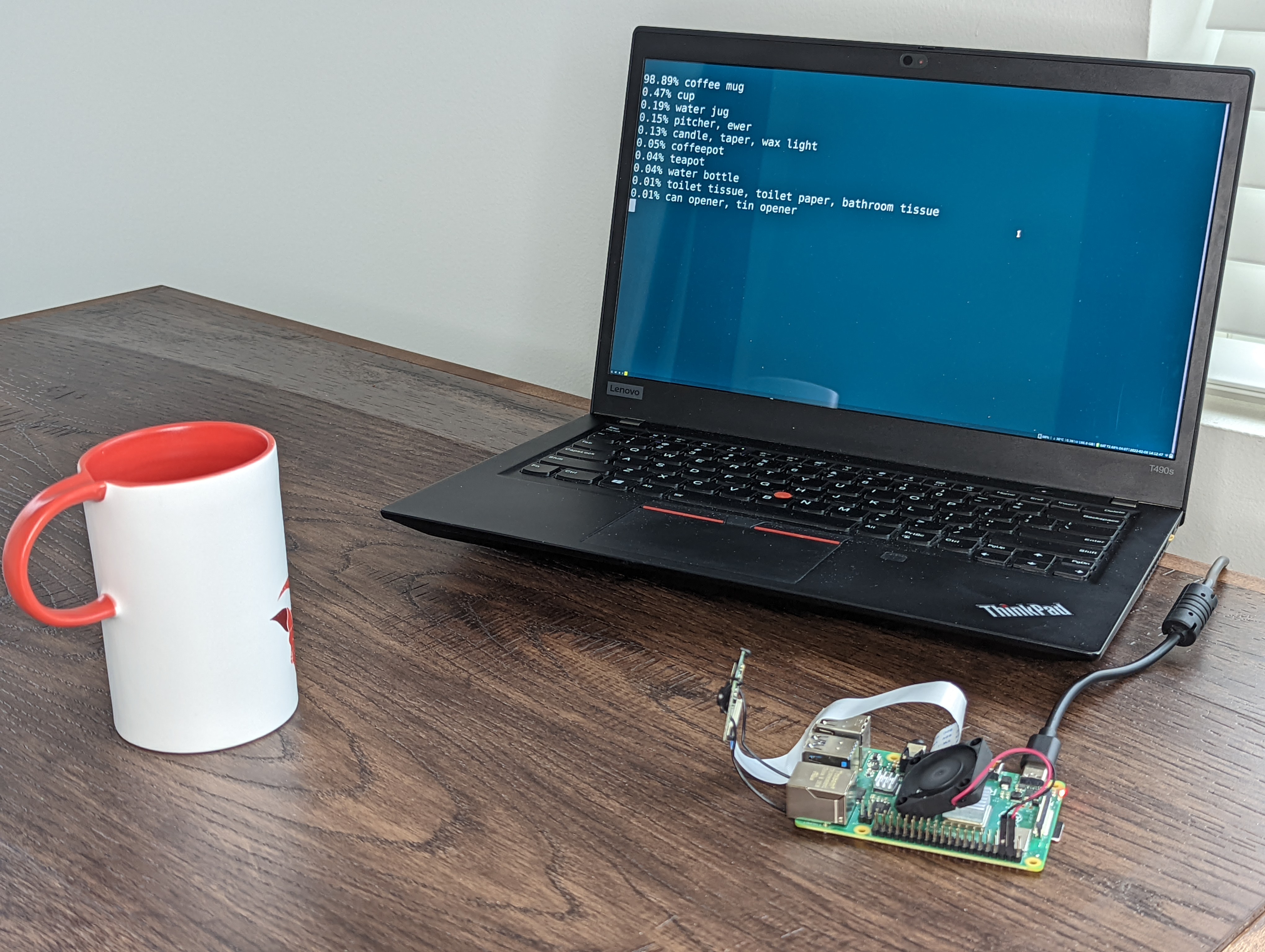
检测到杯子:

故障排除:性能问题
PyTorch 默认会使用所有可用的核心。如果在树莓派上后台运行任何程序,可能会与模型推理产生竞争,导致延迟波动。为了缓解这种情况,您可以减少线程数,这将降低峰值延迟,但会有轻微的性能损失。
torch.set_num_threads(2)
使用 2 threads 替代 4 threads 可以将最佳情况延迟从 60 ms 提高到 72 ms ,但消除了 128 ms 的延迟波动。
下一步操作 ¶
您可以创建自己的模型或微调现有的模型。如果您在 torchvision.models.quantized 中的模型上进行微调,大部分融合和量化的工作已经为您完成,因此您可以直接部署到树莓派上,获得良好的性能。
查看更多:
有关如何量化并融合您的模型的更多信息。
转移学习教程:如何使用迁移学习微调预训练模型以适应您的数据集。