编译自动微分:捕获更大的反向图 torch.compile ¶
创建时间:2025 年 4 月 1 日 | 最后更新时间:2025 年 4 月 1 日 | 最后验证时间:2024 年 10 月 9 日
作者:范西蒙
编译后的 autograd 如何与
torch.compile交互如何使用编译后的 autograd API
如何使用
TORCH_LOGS检查日志
PyTorch 2.4
完成 PyTorch 2.x 编译器简介
阅读 PyTorch 2.x 入门指南中的 TorchDynamo 和 AOTAutograd 部分
概述 ¶
编译 Autograd 是 PyTorch 2.4 中引入的 torch.compile 扩展,允许捕获更大的反向图。
虽然 torch.compile 确实捕获了反向图,但它只部分地这样做。AOTAutograd 组件在编译前捕获反向图,存在某些限制:
前向图断点导致反向图断点
反向钩子没有被捕获
编译 Autograd 通过直接集成到 autograd 引擎中,允许它在运行时捕获完整的反向图,从而解决了这些限制。具有这两个特性的模型应尝试使用编译 Autograd,并可能观察到更好的性能。
然而,编译 Autograd 引入了自己的限制:
在反向传播开始时添加了运行时开销以进行缓存查找
由于捕获范围更大,在 dynamo 中更容易重新编译和图断裂
备注
编译 Autograd 正在积极开发中,并且目前尚不支持所有现有的 PyTorch 功能。有关特定功能的最新状态,请参阅编译 Autograd 着陆页面。
设置
在本教程中,我们将基于这个简单的神经网络模型进行示例。它接受一个 10 维输入向量,通过单个线性层进行处理,并输出另一个 10 维向量。
import torch
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(10, 10)
def forward(self, x):
return self.linear(x)
基本用法
在调用 torch.compile API 之前,请确保将 torch._dynamo.config.compiled_autograd 设置为 True :
model = Model()
x = torch.randn(10)
torch._dynamo.config.compiled_autograd = True
@torch.compile
def train(model, x):
loss = model(x).sum()
loss.backward()
train(model, x)
在上面的代码中,我们创建了一个 Model 类的实例,并使用 torch.randn(10) 生成一个随机的 10 维张量 x 。我们定义了训练循环函数 train ,并用@torch.compile 进行装饰以优化其执行。当调用 train(model, x) 时:
Python 解释器调用 Dynamo,因为这次调用被装饰了
@torch.compile。Dynamo 拦截 Python 字节码,模拟执行并记录操作到图中。
AOTDispatcher禁用钩子并调用自动微分引擎计算model.linear.weight和model.linear.bias的梯度,并将操作记录到图中。使用torch.autograd.Function,AOTDispatcher 重写train的前向和反向实现。电感生成与 AOTDispatcher 前向和反向优化实现相对应的函数。
Dynamo 将优化函数设置为 Python 解释器下次要评估的函数。
Python 解释器执行优化函数,执行
loss = model(x).sum()。Python 解释器执行
loss.backward(),调用自动微分引擎,由于我们设置了torch._dynamo.config.compiled_autograd = True,因此路由到编译后的自动微分引擎。编译后的自动微分引擎计算
model.linear.weight和model.linear.bias的梯度,并将操作记录到图中,包括遇到的任何钩子。在此过程中,它将记录由 AOTDispatcher 重写的反向操作。编译后的自动微分引擎随后生成一个新函数,该函数对应于loss.backward()的完全跟踪实现,并以推理模式使用torch.compile执行它。递归地应用相同的步骤到编译后的 Autograd 图,但这次 AOTDispatcher 不需要对图进行分区。
检查编译后的 autograd 日志
使用 TORCH_LOGS 环境变量运行脚本:
仅打印编译后的 autograd 图,请使用
TORCH_LOGS="compiled_autograd" python example.py为了以牺牲性能为代价打印包含更多张量元数据和重新编译原因的图,请使用
TORCH_LOGS="compiled_autograd_verbose" python example.py
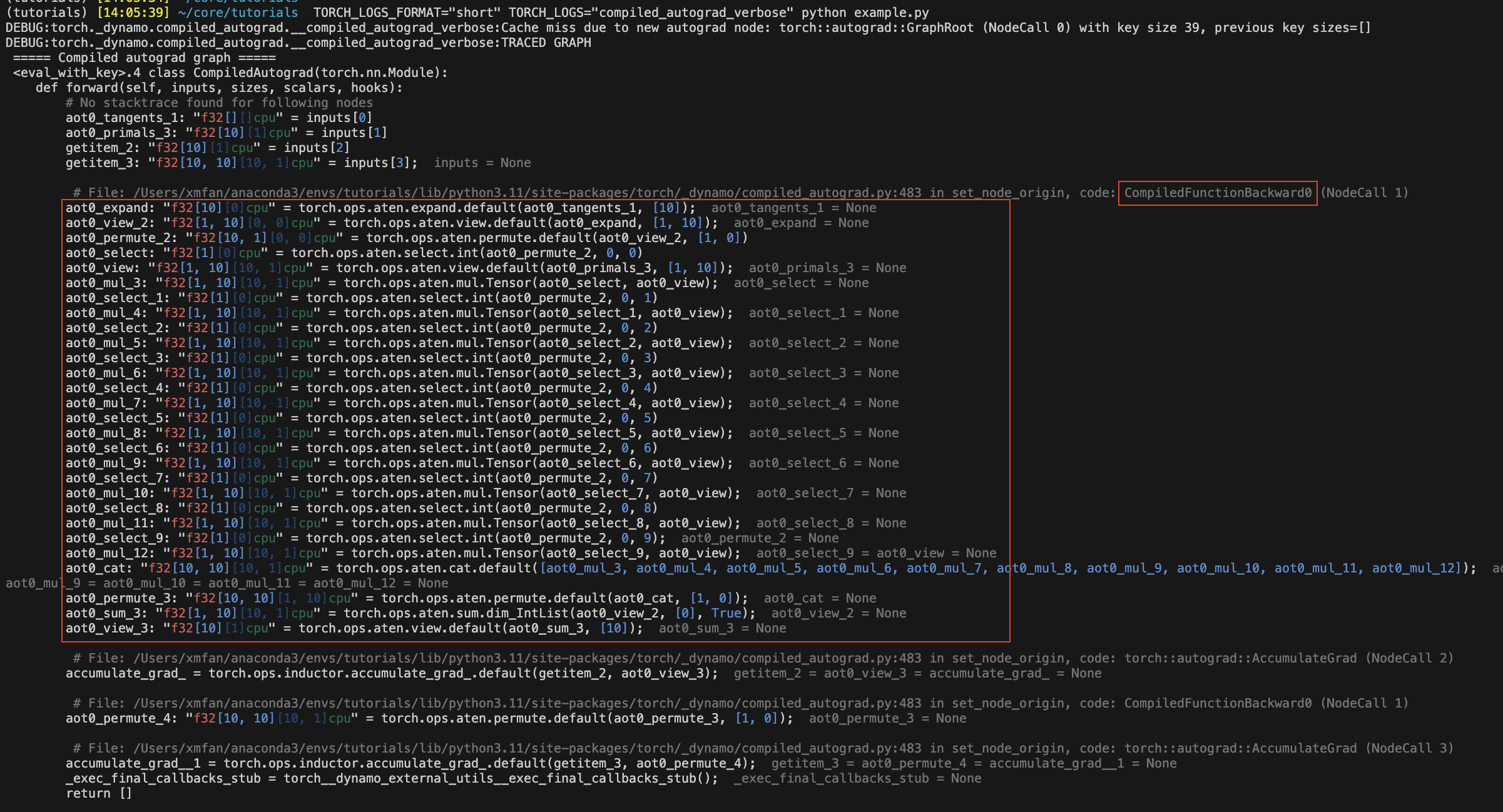
重新运行上面的代码片段,编译后的自动微分图现在应该被记录到 stderr 。某些图节点将带有 aot0_ 的前缀,这些节点对应于之前在 AOTAutograd 反向图 0 中预先编译的节点,例如, aot0_view_2 对应于 id=0 的 AOT 反向图中的 view_2 。
在下面的图片中,红色框封装了由 torch.compile 捕获的 AOT 反向图,该图没有使用编译后的自动微分。
备注
这是我们将要调用 torch.compile 的图,而不是优化后的图。编译后的自动微分本质上生成一些未优化的 Python 代码来表示整个 C++自动微分执行。
使用不同的标志编译正向和反向传递 ¶
您可以为这两个编译使用不同的编译器配置,例如,即使正向中有图断开,反向也可能是一个 fullgraph。
def train(model, x):
model = torch.compile(model)
loss = model(x).sum()
torch._dynamo.config.compiled_autograd = True
torch.compile(lambda: loss.backward(), fullgraph=True)()
或者您可以使用上下文管理器,它将应用于其作用域内的所有 autograd 调用。
def train(model, x):
model = torch.compile(model)
loss = model(x).sum()
with torch._dynamo.compiled_autograd.enable(torch.compile(fullgraph=True)):
loss.backward()
编译 Autograd 解决了 AOTAutograd 的一些限制 ¶
前向传播中的图断裂不再必然导致反向传播中的图断裂:
@torch.compile(backend="aot_eager")
def fn(x):
# 1st graph
temp = x + 10
torch._dynamo.graph_break()
# 2nd graph
temp = temp + 10
torch._dynamo.graph_break()
# 3rd graph
return temp.sum()
x = torch.randn(10, 10, requires_grad=True)
torch._dynamo.utils.counters.clear()
loss = fn(x)
# 1. base torch.compile
loss.backward(retain_graph=True)
assert(torch._dynamo.utils.counters["stats"]["unique_graphs"] == 3)
torch._dynamo.utils.counters.clear()
# 2. torch.compile with compiled autograd
with torch._dynamo.compiled_autograd.enable(torch.compile(backend="aot_eager")):
loss.backward()
# single graph for the backward
assert(torch._dynamo.utils.counters["stats"]["unique_graphs"] == 1)
在第一个案例中,我们看到由于编译函数中的 2 个图断裂,产生了 3 个反向图。而在第二个编译 autograd 案例中,我们看到尽管存在图断裂,仍然追踪到了完整的反向图。
备注
当追踪由编译 Autograd 捕获的反向钩子时,Dynamo 仍然可能在反向传播时发生图断裂。
现在可以捕获反向钩子
@torch.compile(backend="aot_eager")
def fn(x):
return x.sum()
x = torch.randn(10, 10, requires_grad=True)
x.register_hook(lambda grad: grad+10)
loss = fn(x)
with torch._dynamo.compiled_autograd.enable(torch.compile(backend="aot_eager")):
loss.backward()
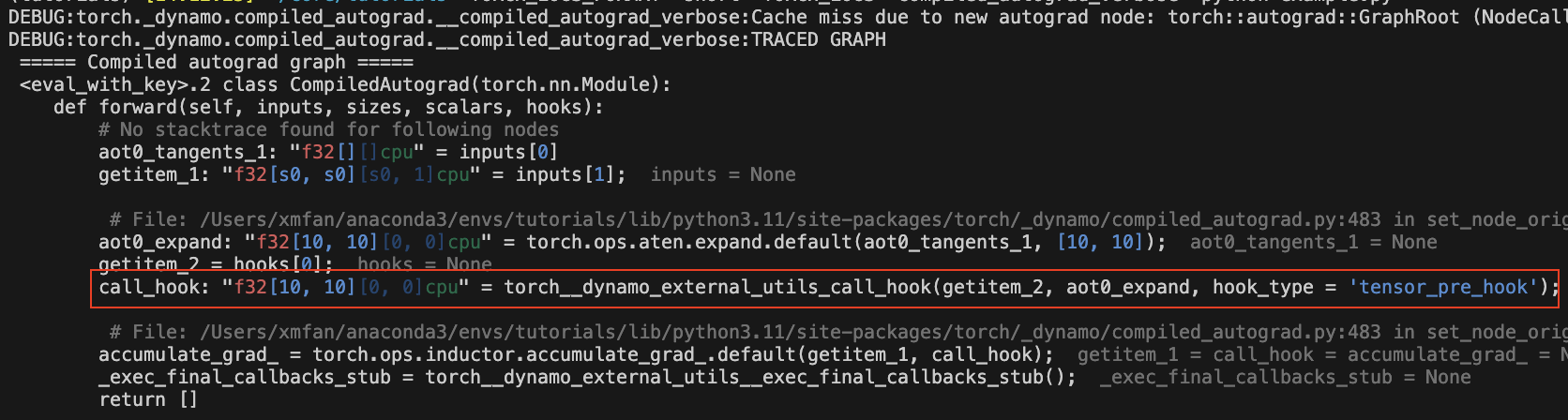
图中应该有一个 call_hook 节点,Dynamo 稍后会将其内联到以下内容中:
编译 Autograd 的常见重新编译原因
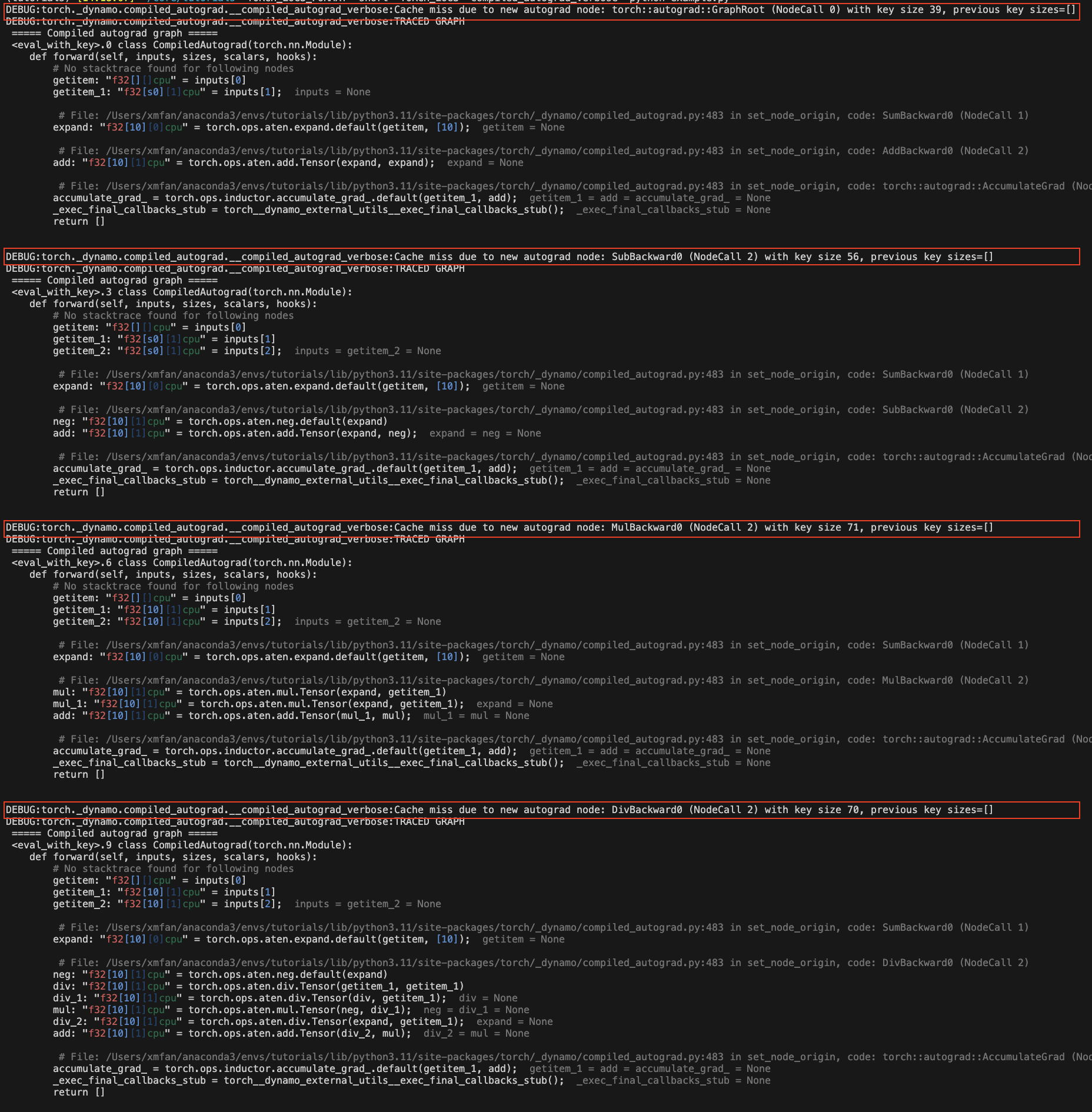
由于损失值 autograd 结构的变化:
torch._dynamo.config.compiled_autograd = True
x = torch.randn(10, requires_grad=True)
for op in [torch.add, torch.sub, torch.mul, torch.div]:
loss = op(x, x).sum()
torch.compile(lambda: loss.backward(), backend="eager")()
在上面的示例中,我们每次迭代都调用不同的运算符,导致 loss 跟踪不同的 autograd 历史。你应该会看到一些重新编译的消息:由于新的 autograd 节点导致的缓存未命中。
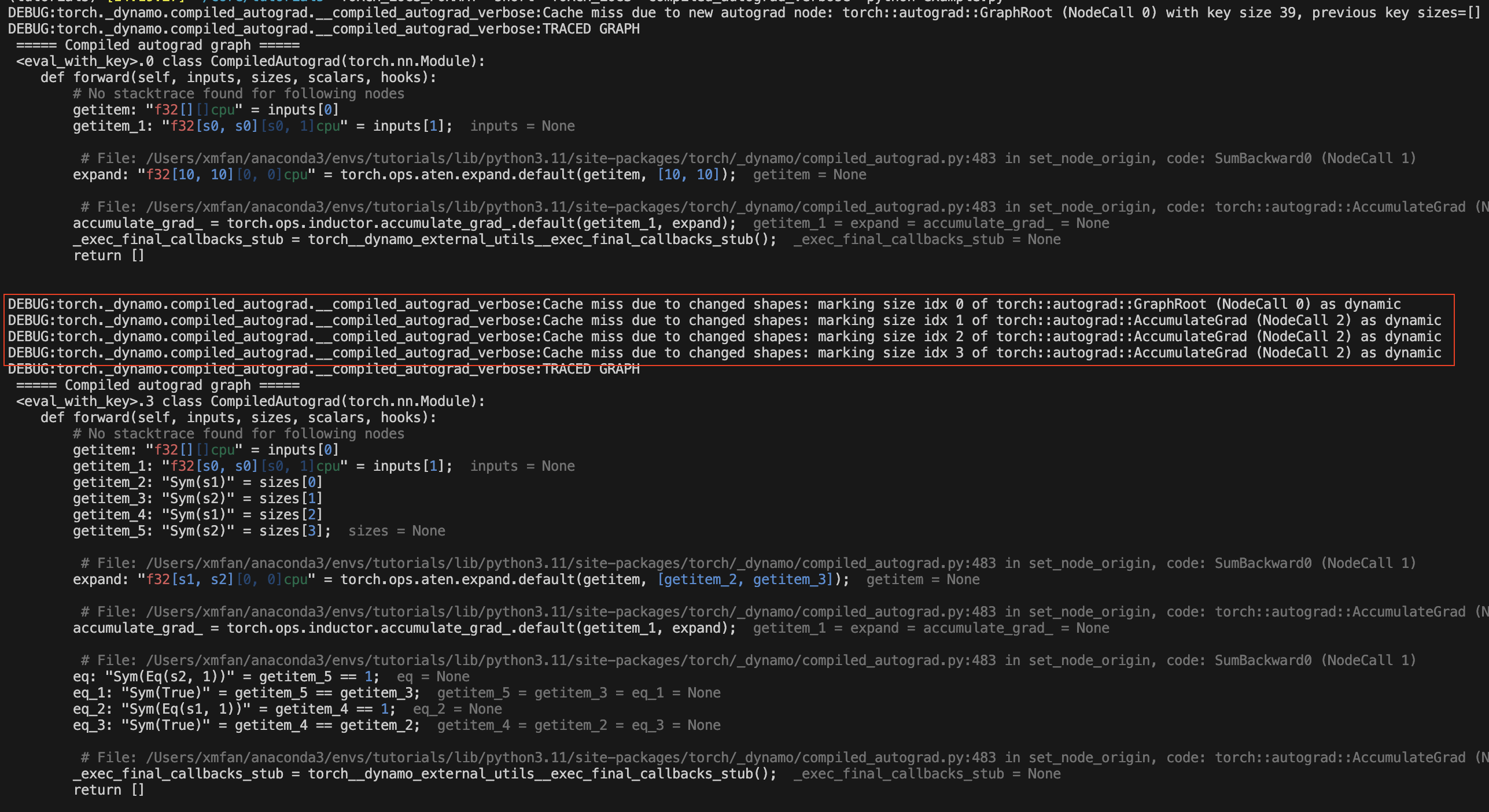
由于张量形状变化:
torch._dynamo.config.compiled_autograd = True
for i in [10, 100, 10]:
x = torch.randn(i, i, requires_grad=True)
loss = x.sum()
torch.compile(lambda: loss.backward(), backend="eager")()
在上面的例子中, x 发生形状变化,编译后的 autograd 将在第一次变化后将 x 标记为动态形状张量。你应该看到重新编译的消息:由于形状变化导致的缓存未命中。
结论 ¶
在本教程中,我们介绍了 torch.compile 的编译 autograd 高级生态系统、编译 autograd 的基础知识和一些常见的重新编译原因。敬请关注 dev-discuss 上的深入探讨。