Hidet 是一个强大的深度学习编译器,它简化了在现代化加速器(例如 NVIDIA GPU)上实现高性能深度学习算子的过程。借助 PyTorch 2.0 中的新特性 torch.compile(...) ,将新型编译器集成到 PyTorch 中比以往任何时候都更加容易——Hidet 现在可以作为 torch.compile(...) 后端来加速 PyTorch 模型,使其成为希望提高模型推理性能的 PyTorch 用户的理想选择,尤其是对于那些需要实现极度优化的自定义算子的用户。
使用 Hidet 编译 PyTorch 模型
要在 PyTorch 中使用 Hidet,您需要首先通过 pip 安装 hidet 包:
pip install hidet
Hidet 集成 PyTorch 作为 torch.compile(...) 后端,遵循自定义后端教程。在编译模型时,您可以指定 hidet 作为 backend 。(注意:需要 PyTorch 版本 2.0+):
torch.compile(..., backend='hidet')
Hidet 将给定的 PyTorch 模型从 torch.fx.Graph 格式转换为内部图表示,并进行一系列优化。Hidet 提供了一些配置优化的选项。例如,我们可以使用 hidet.torch.dynamo_config.use_tensor_core(True) 允许 Hidet 生成利用 NVIDIA GPU 上的 Tensor Cores 的 CUDA 内核,并使用 hidet.torch.dynamo_config.search_space(2) 允许 Hidet 为您的硬件和输入大小搜索最佳算子调度。更多配置可以在 Hidet 的文档中找到。
下面是一个使用 Hidet 编译和优化从 torchvision 预训练的 ResNet50 模型的完整示例:
import hidet
import torch
# Load a pre-trained ResNet50 model
x = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224, device='cuda').half()
model = torch.hub.load(
'pytorch/vision:v0.6.0', 'resnet50', pretrained=True
).cuda().half().eval()
# Configure hidet to use tensor core and enable tuning
hidet.torch.dynamo_config.use_tensor_core(True)
hidet.torch.dynamo_config.search_space(2)
# Compile the model using Hidet
model_opt = torch.compile(model, backend='hidet')
# Check correctness
torch.testing.assert_close(actual=model_opt(x), expected=model(x), rtol=1e-2, atol=1e-2)
# Benchmark
from hidet.utils import benchmark_func
print('eager: {:2f}'.format(benchmark_func(lambda: model(x))))
print('hidet: {:2f}'.format(benchmark_func(lambda: model_opt(x))))
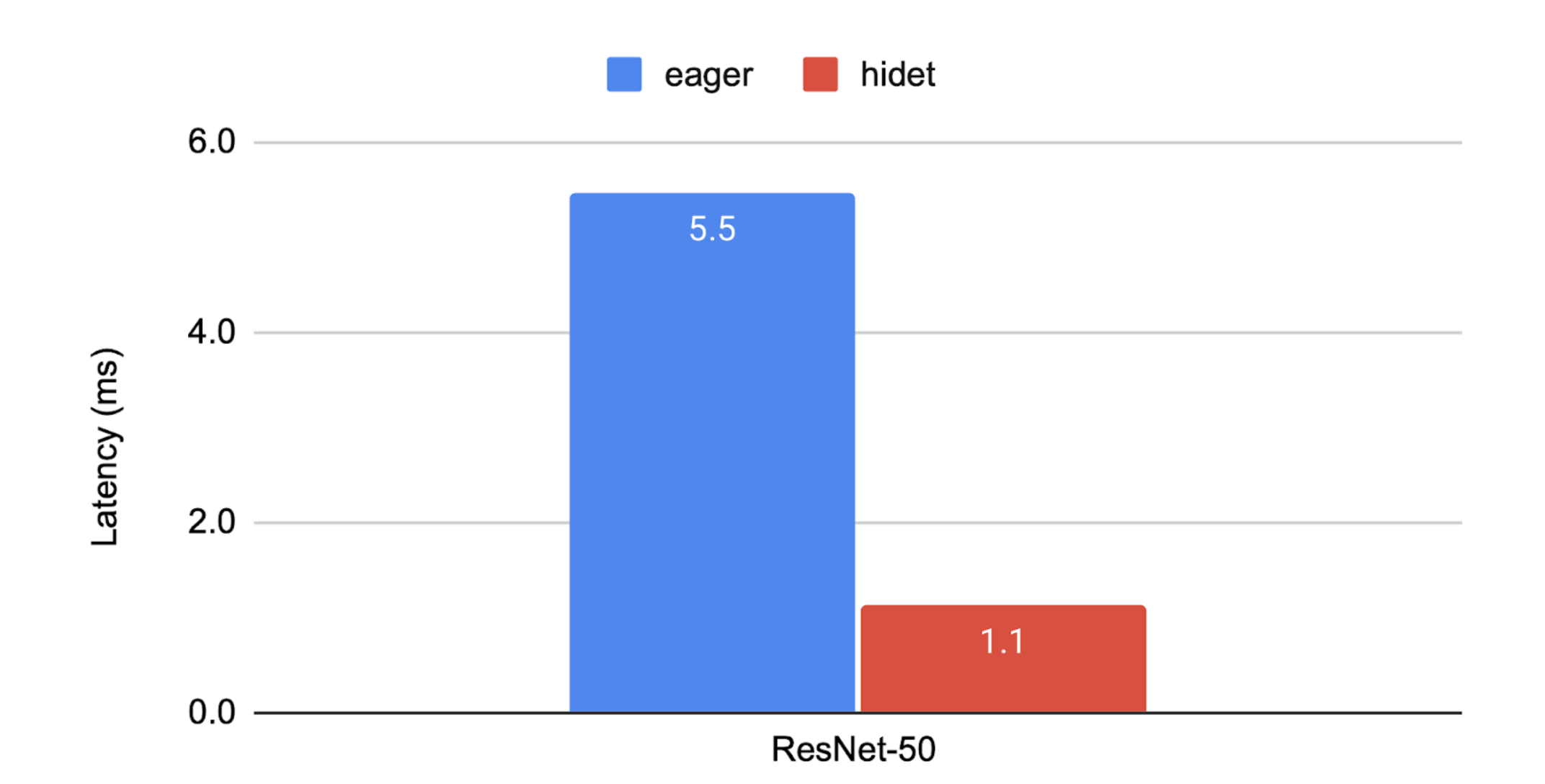
我们鼓励您在自己的 NVIDIA GPU 上尝试上述脚本!如果您在 aws.g5.2xlarge 实例上运行此脚本,您将得到以下图中所示的结果。Hidet 通过能够自动融合多个算子、调整算子调度以及使用 CUDA Graph 来减少框架级开销来实现加速。更多结果可以在 Hidet 和我们的性能跟踪的 ASPLOS’23 出版物中找到。
使用 Hidet 脚本编写自定义算子
Hidet 脚本是实现 Python 中张量算子的一种方法。以下示例展示了如何使用 Hidet 脚本实现一个简单的矩阵乘法,并将其集成到 PyTorch 算子中。
import torch
import hidet
def matmul(m_size, n_size, k_size):
from hidet.lang import f32, attr
from hidet.lang.cuda import threadIdx, blockIdx, blockDim
with hidet.script_module() as script_module:
@hidet.script
def matmul(
a: f32[m_size, k_size],
b: f32[k_size, n_size],
c: f32[m_size, n_size]
):
attr.cuda_grid_dim = ((m_size + 31) // 32, (n_size + 31) // 32)
attr.cuda_block_dim = (32, 32)
i = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x
j = threadIdx.y + blockIdx.y * blockDim.y
if i < m_size and j < n_size:
c[i, j] = 0.0
for k in range(k_size):
c[i, j] += a[i, k] * b[k, j]
ir_module = script_module.ir_module()
func = hidet.driver.build_ir_module(ir_module)
return func
class NaiveMatmul(torch.autograd.Function):
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, a, b):
m, k = a.shape
k, n = b.shape
c = torch.empty([m, n], dtype=a.dtype, device=a.device)
func = matmul(m, n, k)
func(a, b, c)
return c
a = torch.randn([3, 4], device='cuda')
b = torch.randn([4, 5], device='cuda')
c = NaiveMatmul.apply(a, b)
cc = torch.matmul(a, b)
torch.testing.assert_close(c, cc)
可以应用更多优化,请参阅我们的文档中的示例以了解更多信息。
Hidet Script 与 Triton 的比较:Triton 通过引入基于瓦片的编程模型,将并行执行单元从线程变为线程块,极大地简化了 CUDA 编程。然而,这种简化也阻止了张量程序开发者以他们偏好的方式操纵细粒度的计算和内存资源(例如,warp、共享内存)。如果 Triton 编译器本身没有实现,那么使用 Triton 实现需要细粒度控制这些资源的优化将具有挑战性。另一方面,Hidet Script 简化了张量编程,同时仍然允许用户以广泛的灵活性实现自己的优化。值得注意的是,与 Triton 相比,Hidet Script 的更细粒度控制也带来了额外的复杂性。
更多关于 Hidet 的信息
Hidet 起源于由多伦多大学(UofT)EcoSystem 实验室和 AWS 领导的研究项目。作者提出了一种名为任务映射编程范式的全新方法来构建张量程序。它旨在在不牺牲任何优化机会的情况下简化张量编程。现在,Hidet 是一个由 CentML 和 EcoSystem 实验室共同支持的开源项目,旨在为现代加速器(例如 NVIDIA GPU)上的端到端推理提供高效解决方案。
其他资源
- GitHub 仓库:https://github.com/hidet-org/hidet
- Hidet 文档:https://docs.hidet.org
- ASPLOS '23 论文:https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3575693.3575702
- ASPLOS '23 教程:https://centml.github.io/asplos23-tutorial/
致谢
我们要感谢 Jerry Park、Mark Saroufim、Jason Liang 和 Helen Suk 在准备博客文章和文本反馈方面的宝贵帮助。同时,我们还要感谢 Nikita Shulga、Jason Ansel 和 Dmytro Dzhulgakov 对我们在第三方 dynamo 后端注册的 PR https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/93873 的审查和改进。